EdgeL3: Compressing L3-Net for Mote Scale Urban Noise Monitoring
Kumari, S., Roy, D., Cartwright, M., Bello, J.P., Arora, A. EdgeL3: Compressing L3-Net for Mote Scale Urban Noise Monitoring. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Parallel AI and Systems for the Edge (PAISE), 2019.
Abstract
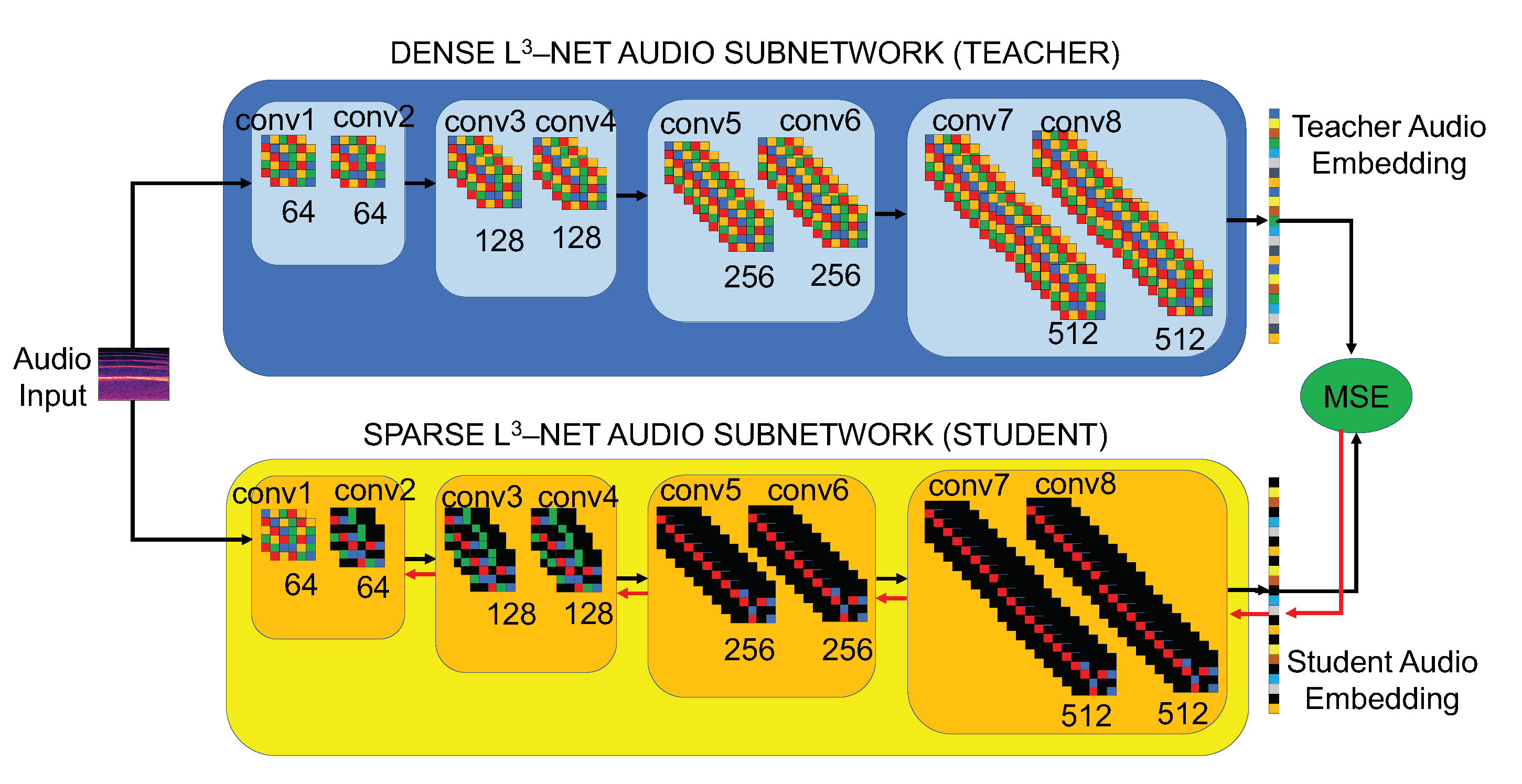
Urban noise sensing in deeply embedded devices at the edge of the Internet of Things (IoT) is challenging not only because of the lack of sufficiently labeled training data but also because device resources are quite limited. Look, Listen, and Learn (L3), a recently proposed state-of-the-art transfer learning technique, mitigates the first challenge by training selfsupervised deep audio embeddings through binary Audio-Visual Correspondence (AVC), and the resulting embeddings can be used to train a variety of downstream audio classification tasks. However, with close to 4.7 million parameters, the multi-layer L3-Net CNN is still prohibitively expensive to be run on small edge devices, such as “motes” that use a single microcontroller and limited memory to achieve long-lived self-powered operation.
In this paper, we comprehensively explore the feasibility of compressing the L3-Net for mote-scale inference. We use pruning, ablation, and knowledge distillation techniques to show that the originally proposed L3-Net architecture is substantially overparameterized, not only for AVC but for the target task of sound classification as evaluated on two popular downstream datasets. Our findings demonstrate the value of fine-tuning and knowledge distillation in regaining the performance lost through aggressive compression strategies. Finally, we present EdgeL3, the first L3-Net reference model compressed by 1-2 orders of magnitude for real-time urban noise monitoring on resourceconstrained edge devices, that can fit in just 0.4 MB of memory through half-precision floating point representation.
Resources
- Code: EdgeL3 python package